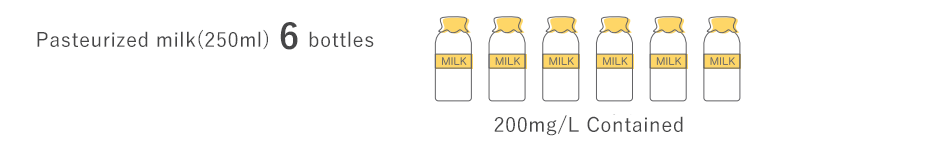
Lactoferrin is a nutrient which was discovered in milk in 1939. In humans, lactoferrin is abundant in breast milk (especially colostrum, the first milk produced after the birth of a baby) and is also found in tears, saliva, and mucus, which are often exposed to the open air in adults. In general, bad bacteria require iron for growth. Lactoferrin is a multifunctional iron-binding glycoprotein known for its ability to bind iron.
This is why the name “lactoferrin” was derived from the combination of “lact (lact) = milk” and “ferrin (ferrin) = iron. Lactoferrin is also called “red protein” because of its slightly reddish color.